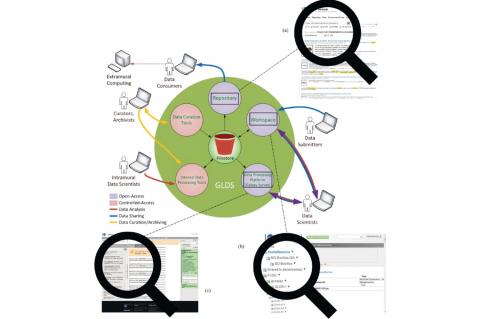
Omics data sharing is crucial to the biological research community, and the last decade or two has seen a huge rise in collaborative analysis systems, databases, and knowledge bases for omics and other systems biology data. We assessed the "FAIRness" of NASA's GeneLab Data Systems (GLDS) along with four similar kinds of systems in the research omics data domain, using 14 FAIRness metrics. The range of overall FAIRness scores was 6-12 (out of 14), average 10.1, and standard deviation 2.4. The range of Pass ratings for the metrics was 29-79%, Partial Pass 0-21%, and Fail 7-50%. The systems we evaluated performed the best in the areas of data findability and accessibility, and worst in the area of data interoperability. Reusability of metadata, in particular, was frequently not well supported. We relate our experiences implementing semantic integration of omics data from some of the assessed systems for federated querying and retrieval functions, given their shortcomings in data interoperability. Finally, we propose two new principles that Big Data system developers, in particular, should consider for maximizing data accessibility. Read the full publication at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30815061/

